Exploring the ICMP Protocol
☰ Section: Network | ⚀ Posted: 2025-04-29 02:27:04 | ⚀ Updated: 2025-04-29 02:27:04 DALL-E via ChatGPT - powered by OpenAI
DALL-E via ChatGPT - powered by OpenAI
Unveiling the Backbone of Network Communication
In the vast realm of computer networks, where seamless communication is paramount, the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) emerges as a silent workhorse. Often operating in the background, ICMP plays a crucial role in facilitating communication between devices, ensuring the reliability and efficiency of data transmission. This article dives deep into the nuances of the ICMP protocol, shedding light on its functions, significance, and its impact on the interconnected world we navigate.
Despite its behind-the-scenes nature, ICMP becomes highly visible in troubleshooting scenarios — think of tools like ping and traceroute, which rely heavily on ICMP messages to diagnose network issues. Its ability to report errors and provide feedback about IP packet processing makes it an indispensable part of any network professional's toolkit. As we delve deeper, you'll discover how ICMP not only supports network health but can also reveal potential vulnerabilities when misused.
Understanding ICMP: The Messenger of the Network
Key Functions of ICMP
ICMP, a fundamental part of the Internet Protocol (IP) suite, serves as the messenger of the network, carrying messages that convey information about network conditions, errors, and troubleshooting. It operates at the Network Layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model, playing a pivotal role in the reliable delivery of data across interconnected devices.
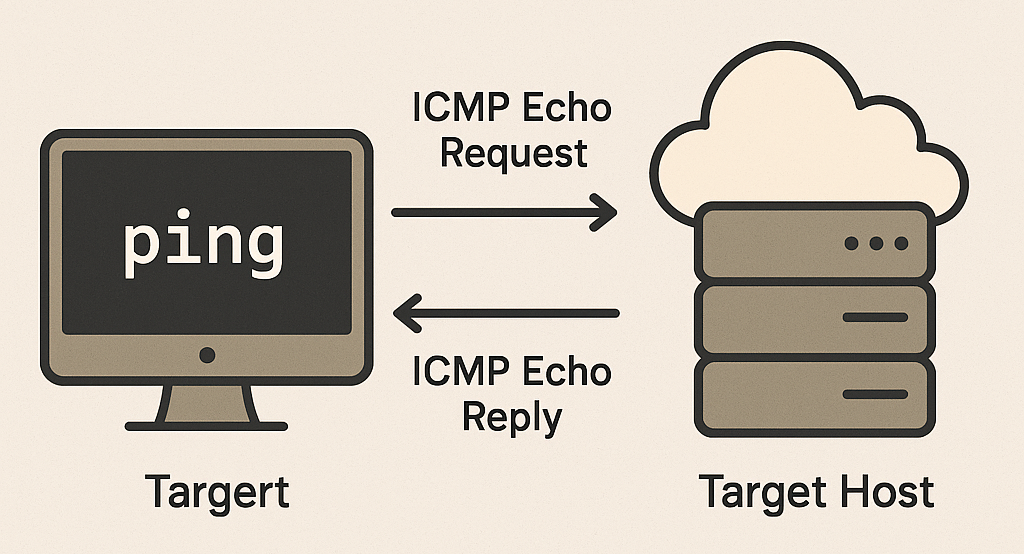
Ping and Echo Requests:The ubiquitous "ping" utility utilizes ICMP Echo Request and Echo Reply messages. These messages are used to check the reachability of a host, measure round-trip time, and diagnose network connectivity issues.
Error Reporting:ICMP is instrumental in reporting errors that occur during the transmission of IP packets. When a network issue arises, ICMP packets are generated and sent back to the source to inform about the problem, allowing for rapid troubleshooting.
Time Exceeded Messages:ICMP Time Exceeded messages are generated when a packet traverses routers for too long without reaching its destination. This helps identify potential routing loop issues or excessive network latency.
Destination Unreachable Messages:If a router or gateway cannot forward an IP packet to its destination, ICMP Destination Unreachable messages are generated. This provides valuable information to the sender about the nature of the issue, such as network congestion or an unreachable host.
Redirect Messages:ICMP Redirect messages are used by routers to inform hosts about a more optimal route for a given destination. When a host sends packets through an inefficient path, a router can send a redirect to suggest a better gateway, improving network efficiency and routing decisions.
Ping: The Everyday Application of ICMP
 ChatGPT - powered by OpenAI
ChatGPT - powered by OpenAI
The ping command, widely used in network diagnostics, sends ICMP Echo Request messages to a target host. The host, if reachable, responds with an ICMP Echo Reply, allowing administrators to assess network connectivity and response times.
It is an invaluable tool for network administrators when troubleshooting, aiding in the identification of connectivity issues, measuring latency, and assessing the overall health of a network.
While simple in concept, ping can reveal a wealth of information. Repeated packet loss may indicate congestion or faulty hardware, while high or fluctuating round-trip times could point to routing inefficiencies or overloaded systems. Combined with other tools (e.g. wireshark), ping becomes a foundation for deeper network analysis and monitoring strategies.
ICMP and Network Security
Potential for Abuse
While ICMP is essential for network troubleshooting, some security concerns exist, particularly with the potential for abuse in denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. Network administrators must implement security measures to mitigate these risks.
Maybe you can’t entirely disable ICMP, but you can definitely limit its exposure. Rate-limiting ICMP Echo Requests or dropping suspicious patterns can help avoid (D)DoS amplification attacks, especially in publicly accessible environments. Smart filtering keeps diagnostics possible while reducing the attack surface.
Firewall Considerations
Configuring firewalls to allow necessary ICMP traffic while blocking potentially harmful packets is a common practice to balance security and functionality.
Putting a server into so-called "stealth mode" by dropping all ICMP traffic might seem secure, but it can lead to unnecessary retransmissions, longer timeouts, and confusion during diagnostics. Instead, it's often better to configure the packet filter to respond appropriately to specific ICMP types—like Echo Requests, Destination Unreachable, or Time Exceeded—preserving network transparency without sacrificing control.
In the End ...
ICMP, often operating in the background, is the unsung hero of network communication. Its role in error reporting, network troubleshooting, and connectivity assessment cannot be overstated. As we navigate the complexities of the digital landscape, understanding the functions and significance of the ICMP protocol is essential for network administrators and enthusiasts alike.
It remains a fundamental tool in ensuring the reliability and efficiency of data transmission across the interconnected web we rely on daily. For more information about the ICMP protocol see the relating Request for Comments.
Got some light into the dark? Let's hope the lesson is clear.
Have lot of Fun ...
.m0rph
-----BEGIN GEEK CODE BLOCK----- GIT e+ d-- s++:++ a++ G++ C+++ M-- W+++ L++++>$ P+++ E--- W+++ N++ o+ PS+++ PE+++ Y++ PGP++ !DI t++ 5-- X++ R++ tv- b-(++) h+ r- y(++)- -----END GEEK CODE BLOCK-----